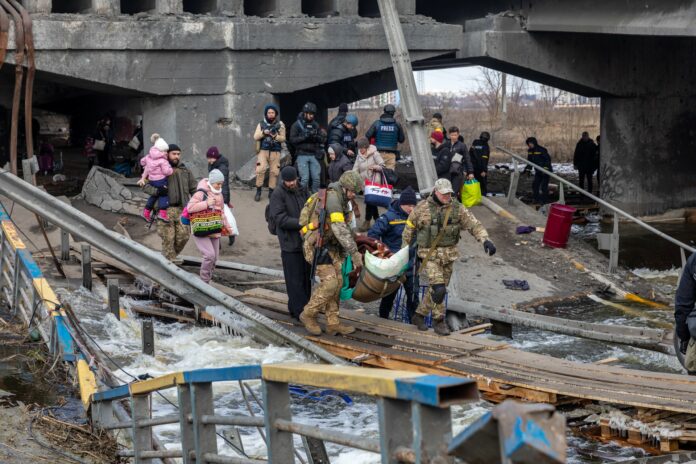
Over the past five decades, the number of disasters has increased five times, driven by climate change and extreme weather patterns, among other factors. In these scenarios, a timely response is vital and significantly impacts public safety. However, the dynamic and unpredictable nature of disasters poses a significant challenge for technical solutions.
Honda Research Institute Europe (HRI-EU), a renowned center for advanced research in intelligent systems, has successfully tested a new solution for mapping evacuation routes for people fleeing from natural disasters, such as earthquakes and floods.
The institute researchers worked with quantum computing specialists at Terra Quantum Group, a leading quantum technology company based in Germany and Switzerland, to use hybrid quantum machine learning to develop a system that could improve mobility challenges in challenging conditions. In the joint project, the team evaluated the potential use of hybrid quantum technologies for optimizing evacuation routes during emergencies.
Terra Quantum has an innovative approach to offer real-time optimal escape routes for people fleeing a disaster in their vehicles. By leveraging its unique IP, algorithms, and Quantum Machine Learning technology, it predicts efficient dynamic escape routes, minimizing evacuation times. Quantum algorithms are inherently flexible, adaptable, and scalable. They could become invaluable for managing crowd flows at large-scale public events or during natural disasters.
“Identifying realistic problems where quantum technologies may unfold their potential constitutes one of the biggest challenges in the field today. This work represents a promising step in that direction and shows how to employ hybrid quantum-classical learning architectures in a real-world use case,” said Dr. Sebastian Schmitt, Principal Scientist at HRI-EU.
As part of the Proof of Concept (POC), an earthquake scenario was simulated in the town of Furubira, Japan. The novel solution demonstrated very promising results, predicting efficient dynamic escape routes for vehicles and, therefore, minimizing evacuation times.
The team says the quantum computing solution already shows competitive efficiency compared to traditional methods, even when simulated on classical hardware. It uses quantum machine learning and requires only local information, which amounts to less than 1% of the map information, to make decisions. This is particularly useful in emergencies with a lot of uncertainty.
The solutions are currently obtained from quantum simulations that are run on classical computing hardware. However, there’s a possibility of extending this application to be executed on large-scale quantum computing hardware in the future.
Researchers say their approach can integrate with existing platforms like Google Maps and future technologies like drones and satellite data. This service could enhance a car’s GPS navigation algorithms and incorporate data on traffic flow, congestion, blocked roads, and weather hazards.
The next step is to scale the technology for larger cities and regions and incorporate more variables and complexities to enhance their effectiveness.
Journal reference:
- Nathan Haboury, Mo Kordzanganeh, Sebastian Schmitt, Ayush Joshi, Igor Tokarev, Lukas Abdallah, Andrii Kurkin, Basil Kyriacou, Alexey Melnikov. A supervised hybrid quantum machine learning solution to the emergency escape routing problem. arXiv, 2023; DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2307.15682
