It was assumed that all stellar nurseries across every galaxy must look more or less the same, but this is not the case. Instead, stellar nurseries change from place to place, suggests a new survey.
Using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), a team of astronomers completed the first census of molecular clouds in the nearby Universe. The survey revealed that stellar nurseries are diverse as the people, homes, neighborhoods, and regions that make up our world.
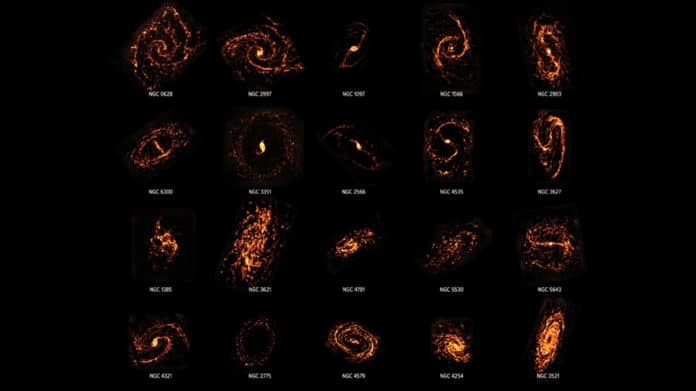
Each stellar nursery in the Universe can form thousands or even tens of thousands of new stars during its lifetime. Between 2013 and 2019, astronomers on the PHANGS– Physics at High Angular Resolution in Nearby GalaxieS– project conducted the first systematic survey of 100,000 stellar nurseries across 90 galaxies in the nearby Universe to get a better understanding of how they connect back to their parent galaxies.
In this survey, astronomers, for the first time, have ever taken millimeter-wave images of many nearby galaxies that have the same sharpness and quality as optical pictures. In addition, the photos revealed the molecular clouds that form those stars.
Eva Schinnerer, an astronomer at the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy (MPIA) and principal investigator for the PHANGS collaboration, said, “To understand how stars form, we need to link the birth of a single star back to its place in the Universe. It’s like linking a person to their home, neighborhood, city, and region. For example, if a galaxy represents a city, then the neighborhood is the spiral arm, the star-forming unit, and nearby galaxies in the region. These observations have taught us that the “neighborhood” has small but pronounced effects on where and how many stars are born.”
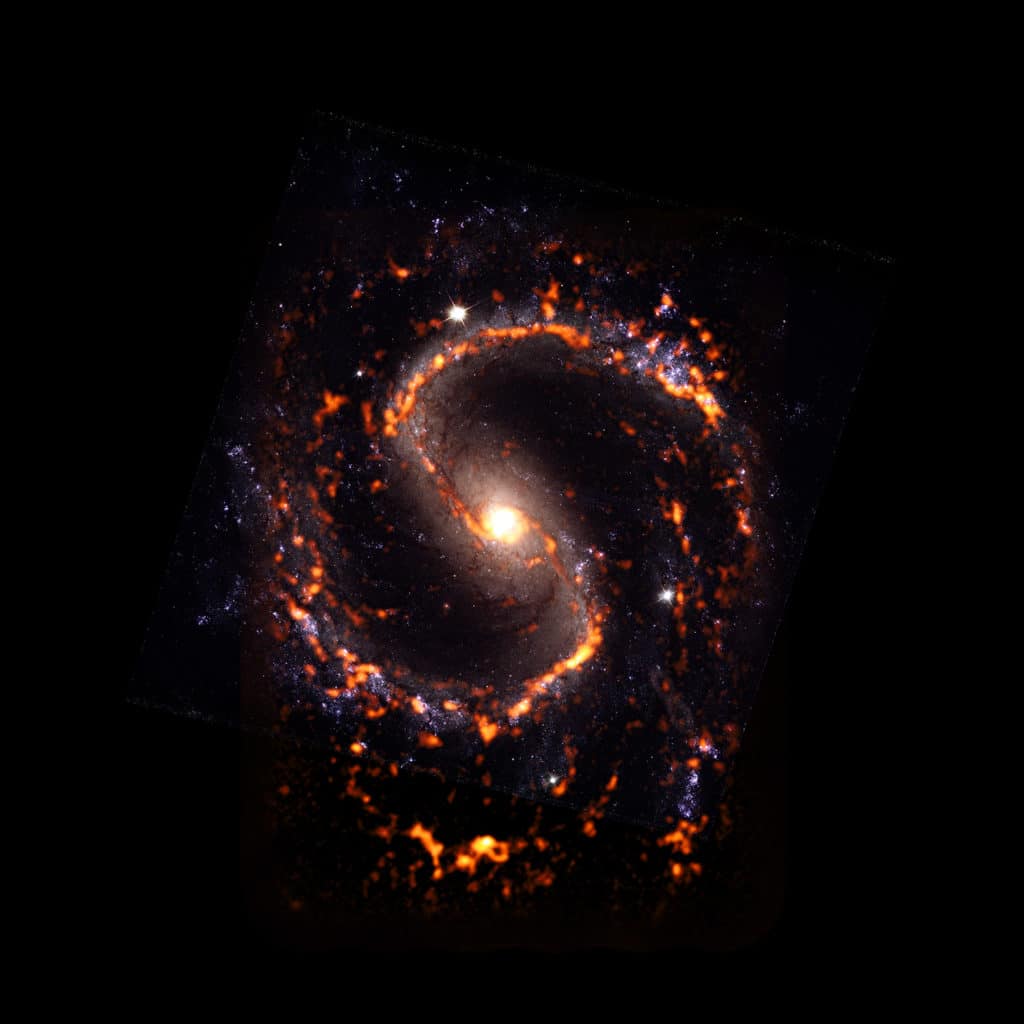

Later, the team observed similarities and differences in the molecular gas properties and star formation processes of galaxy disks, stellar bars, spiral arms, and galaxy centers. Doing so would help them better understand star formation in different types of galaxies. They confirmed that the location, or neighborhood, plays a critical role in star formation.
Guillermo Blanc, an astronomer at the Carnegie Institution for Science and a co-author on the paper, said, “By mapping different types of galaxies and the diverse range of environments that exist within galaxies, we are tracing the whole range of conditions under which star-forming clouds of gas live in the present-day Universe. This allows us to measure the impact that many different variables have on the way star formation happens.”
Joseph Pesce, National Science Foundation’s program officer for NRAO/ALMA, said, “How stars form, and how their galaxy affects that process, are fundamental aspects of astrophysics. The PHANGS project utilizes the exquisite observational power of the ALMA observatory and has provided remarkable insight into the story of star formation in a new and different way.”
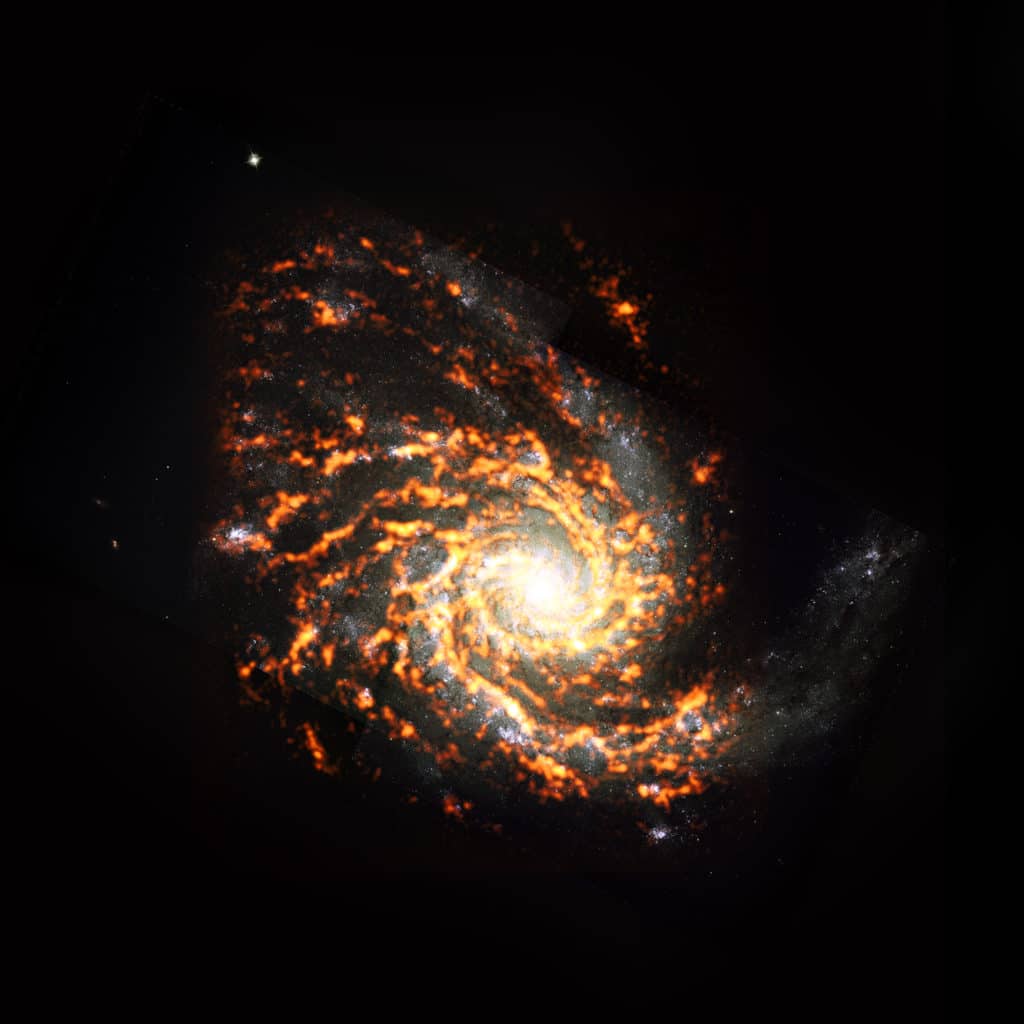

Annie Hughes, an astronomer at L’Institut de Recherche en Astrophysique et Planétologie (IRAP), added that this is the first time scientists have a snapshot of what star-forming clouds are really like across such a broad range of different galaxies. “We found that the properties of star-forming clouds depend on where they are located: clouds in the dense central regions of galaxies tend to be more massive, denser, and more turbulent than clouds that reside in the quiet outskirts of a galaxy. The lifecycle of clouds also depends on their environment. How fast a cloud forms stars and the process that ultimately destroys the cloud both seem to depend on where the cloud lives.”
Erik Rosolowsky, Associate Professor of Physics at the University of Alberta and a co-author on the research, said, “The PHANGS project is a new form of cosmic cartography that allows us to see the diversity of galaxies in a new light, literally. We are finally seeing the diversity of star-forming gas across many galaxies and can understand how they change over time. It was impossible to make these detailed maps before ALMA. This new atlas contains 90 of the best maps ever made that reveal where the next generation of stars is going to form.”
“This is the first time we have gotten a clear view of the population of stellar nurseries across the whole nearby Universe. In that sense, it’s a big step towards understanding where we come from. However, while we now know that stellar nurseries vary from place to place, we still do not know why or how these variations affect the stars and planets formed. These are questions that we hope to answer shortly.”
Journal Reference:
- Adam K. Leroy et al. PHANGS-ALMA: Arcsecond CO(2-1) Imaging of Nearby Star-Forming Galaxies. arXiv:2104.07739