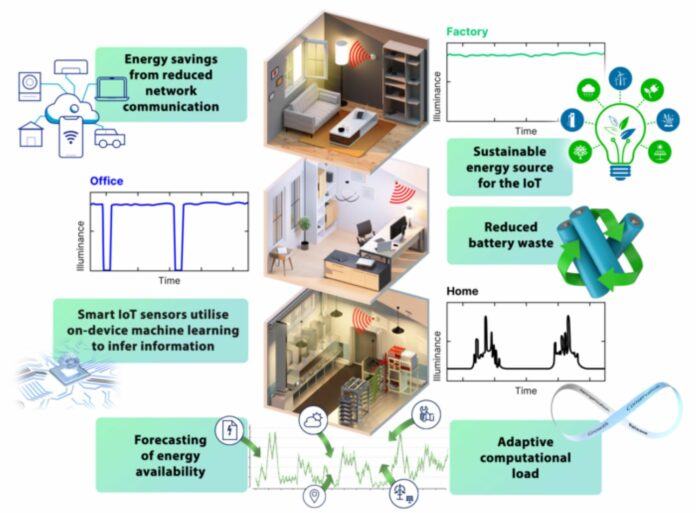
As the number of Internet of Things devices is rapidly increasing, there is an urgent need for sustainable and efficient energy sources and management practices in ambient environments. In response, Newcastle University researchers have created environmentally friendly, high-efficiency photovoltaic cells that harness ambient light to power Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
The research team from the School of Natural and Environmental Sciences (SNES), under the direction of Dr. Marina Freitag, developed dye-sensitized photovoltaic cells based on a copper(II/I) electrolyte, achieving an unprecedented power conversion efficiency of 38% and 1.0V open-circuit voltage at 1,000 lux (fluorescent lamp). The cells, which are safe for the environment and non-toxic, raise the bar for reusable energy sources in natural settings.
Dr. Marina Freitag, Principal Investigator at SNES, Newcastle University, said: “Our research marks an important step towards making IoT devices more sustainable and energy-efficient. By combining innovative photovoltaic cells with intelligent energy management techniques, we are paving the way for a multitude of new device implementations that will have far-reaching applications in various industries.”
Scientists also created a ground-breaking energy management technique to foresee changing deployment circumstances and adjust the computing burden of IoT sensors accordingly. This technique uses long short-term memory (LSTM) artificial neural networks. With the help of this dynamic energy management system, the energy-harvesting circuit may run as efficiently as possible while reducing power losses or brownouts.
This ground-breaking study reveals how artificial intelligence and ambient light as a power source can work together to allow the next wave of Internet of Things devices. The high-efficiency ambient photovoltaic cells that power the energy-efficient IoT sensors may dynamically alter their energy use based on LSTM predictions, leading to significant energy savings and decreased network communication needs.
Journal Reference:
- Michaels, H., Rinderle, M., Benesperi, I., Freitag, R., Gagliardi, A., & Freitag, M. (2023). Emerging Indoor Photovoltaics for Self-Powered and Self-Aware IoT Towards Sustainable Energy Management. Chemical Science. DOI: 10.1039/d3sc00659j