The process of mixing powder is crucial to many different industries. Discrete element method (DEM) numerical simulations have been frequently applied to powder-mixing process analysis. The high computing cost of the DEM simulation is currently one of its drawbacks, though.
Recently, there has been a lot of interest in high-speed computing techniques that integrate numerical simulations with machine learning models. Nevertheless, studies have yet to be conducted on high-speed computing techniques for powder mixing that consider the motions of individual particles.
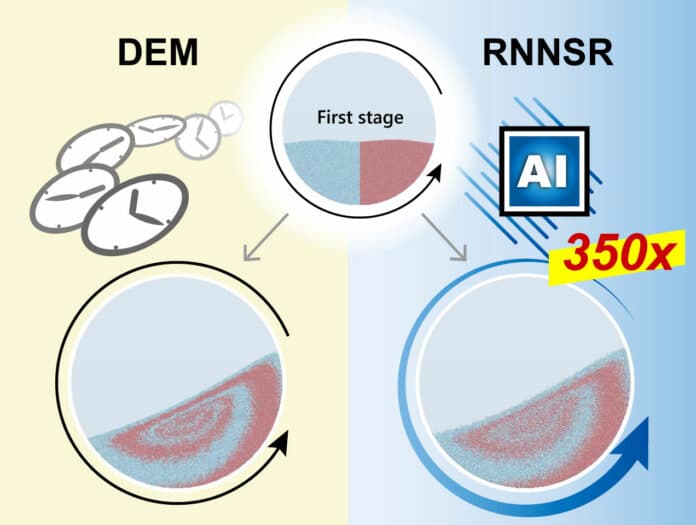
A research team led by Associate Professor Hideya Nakamura, Associate Professor Shuji Ohsaki, Professor Satoru Watano, and Ph.D. student Naoki Kishida from the Graduate School of Engineering at Osaka Metropolitan University has developed a new simulation method using AI. The model, named- recurrent neural network with stochastically calculated random motion (RNNSR)- enables a long-time-scale powder mixing simulation with low computational cost and high accuracy.
This approach maintains the same level of precision as traditional methods but speeds up calculations by about 350 times. It is designed to learn individual particle dynamics with periodicity from short-term DEM simulation results and predict powder mixing for a more extended period.
The model combines a recurrent neural network and a stochastic model to predict convective and diffusive mixing.
The degree of powder mixing, particle velocity, and granular temperature in the simulation results produced using the RNNSR and DEM were similar. Additionally, it was shown that rapid computation in powder-mixing simulations is possible with the RNNSR.
Associate Professor Hideya Nakamura said, “We have successfully harnessed our knowledge in powder technology, which we have honed over many years, and combined it with machine learning to rapidly predict the unique behavior of complex powders. We want to build upon this achievement to contribute to the future of industries seeking to enhance product quality and streamline production.”
Journal Reference:
- Naoki Kishida, Hideya Nakamura, Shuji Ohsaki, Satoru Watano. Development of ultra-fast computing method for powder mixing process. Chemical Engineering Journal. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2023.146166