Until now, alcohol and a series of other intoxicating goods are often blamed as one of the main factors that cause accidents. However, a new study reveals that the technology onboard the cars – such as the infotainment systems designed to make driving even safer – could be exponentially more dangerous.
This interesting research was conducted by IAM RoadSmart, the largest independent British charity engaged in road safety. It found that distractions caused by in-vehicle infotainment systems – like Android Auto and Apple CarPlay – compromise driver response times more than alcohol, cannabis, and smartphone use while driving.
In their study, the team tested the reaction times of motorists according to the actions taken while driving. And the shocking results have shown that slower reaction times caused by drivers using infotainment systems at highway speeds have increased average stopping distances between four and five lengths of the car. It is also found that drivers took their eyes off the road for as long as 16 seconds while driving, and using touch control resulted in reaction times that were even worse than texting while driving.
During the study, drivers were asked to complete a series of three drives on the same simulated test route to assess the level of impact of Android Auto and Apple CarPlay. On the first run, the drivers did not interact with the system. Then on subsequent runs, drivers interacted with the system using voice control only and then using touch control only. Both methods of control were found to significantly distract drivers. However, the touchscreen control is the more distracting of the two methods.
Many drivers realized it was unable to maintain a constant distance from the vehicle that preceded them, as well as more likely to deviate outside of their lane.
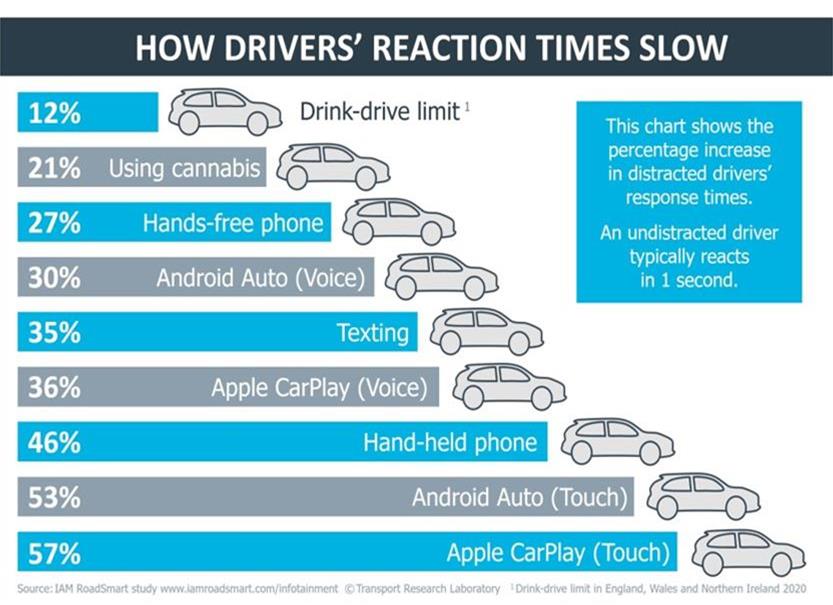
The above graph shows how the continuous use of infotainment systems is far more dangerous than driving under the influence of cannabis or alcohol. According to the data processed by the IAM RoadSmart, reaction times were about 53-57% increased when using the infotainment screens, which is worse than under the influence of alcohol.
“We’re now calling on industry and government to openly test and approve such systems and develop consistent standards that genuinely help minimize driver distraction,” said Neil Greig, policy and research director, IAM RoadSmart. “While we would like to see a review of these systems in the future, we’d encourage owners of vehicles fitted with these systems to use them in the safest possible way, including setting everything up before starting a journey.”
