A new approach to concurrently introduce both therapeutic drugs and cancer-fighting heat into tumors has been discovered. This oncoming research on hairy nanoparticles made with light-sensitive materials that assemble themselves could become “nano-carriers” and will open new doors in cancer research.
That is one potential application for another innovation that joins water-repulsing yet light-touchy and water-retaining materials into polymeric nano-reactors for making photograph-responsive gold nanoparticles.
In this, the light of particular wavelengths causes the nanoparticles to collect and dismantle on request, permitting the dynamic association of the nanoparticles for keen in vitro to tranquilize discharge. By incorporating chemotherapy particles in the nanoparticle structures when they are collected, the atoms could be drawn into tumors and afterward discharged with a light at a shorter wavelength that triggers dismantling through photograph cleavage.
Notwithstanding such dynamic self-gathering and dismantling, the epitome and arrival of chemotherapy atoms could likewise be accomplished by a reversible covalent holding of anticancer medications to the polymeric “hairs” arranged on the surface of nanoparticles. Thereby engrossing a similar light that triggers the medication discharge, the gold nanoparticles could likewise warm the malignancy cells, giving a twofold punch.

Image shows vials containing samples of hairy nanoparticles. The right and left images contain photo-responsive polymer-capped gold nanoparticles prior to and after self-assembly, respectively. The center vial shows dye released from self-assembled gold nanoparticles. The nanoparticles are made with light-sensitive materials that assemble and disassemble themselves when exposed to light of different wavelengths. (Credit: Rob Felt, Georgia Tech)
In an exhaustive scope of different applications, the nanoparticle self-get-together process could likewise be activated by natural elements, including temperature, pH, or dissolvable extremity, by reasonably planning the polymeric hairs.
During the study, scientists used gold nanoparticles, in any case, the procedure could likewise make self-collected nanoparticles from an assortment of metals and metal oxides. Immediately by sewing the surface of nanoparticles with water-engrossing polymers containing close infrared responsive parts, the medication discharge could be performed in vivo.
Here, the circular gold nanoparticles can be superseded with more perplexing formed nanomaterials, for example, empty nanoparticles, nanorods, or nanotubes, to render a superior assimilation of close infrared light to enter natural tissues.
Notwithstanding, no such testing of these nanoparticles has been done as such far in living cells or creatures.
Zhiqun Lin, an educator in the Georgia Tech School of Materials Science and Engineering, stated, “We imagine that these photograph responsive polymer-topped gold nanoparticles would one be able to day fill in as nano-bearers for sedate conveyance into the body utilizing our powerful and reversible process for gathering and dismantling.”
“Utilized as a part of disease treatment, this procedure could build the effect of a treatment by warming the growth cells while bringing the medication compound into the tumor.”
Promote in this examination they found that, under the light, the congregations of photograph delicate nanoparticles isolate over a time of hours at a rate that can be controlled by the force and wavelength of the light.
Lin specified the reason, “On the grounds that the dismantling can be turned on and off voluntarily, we could give a planned arrival of the medication by controlling the short-wavelength light introduction.”
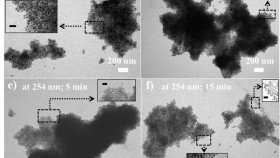
This figure shows the evolution of light-enabled reversible self-assembly of gold nanoparticles made with light-sensitive materials. (Courtesy Zhiqun Lin laboratory).
Capably considered these shaggy nanoparticles are manufactured around a modest center of beta-cyclodextrin from which polymer chains of poly(acrylic acid)- square poly(7-methylacryloyloxy-4-methyl coumarin) (PAA-b-PMAMC) are developed. That material draws in water-dissolvable metal forerunners, which utilize the space inside the polymer hairs as nanoreactors to frame gold nanoparticles.
To these inward structures, which are hydrophilic PAA polymers, the analysts include hairs produced using the hydrophobic monomer MAMC. These materials are touchy to light and make the nanoparticles to self-gather through a photograph dimerization process that is crosslinking when subjected to light at a wavelength of 365 nanometers.
This get-together process can be dependably turned around on request utilizing a shorter wavelength at 254 nanometers.
Lin stated, “Once the polymer chains from contiguous gold nanoparticles start to photograph crosslink, they unite nanoparticles through a self-gathering procedure to produce substantial congregations of nanoparticles.”
“This procedure is totally reversible and can be rehashed in numerous cycles.”
The examination group consolidated color particles into the self-collected nanoparticles to recreate what may be done to fuse and discharge chemotherapy specialists. An attractive oxide material fused into the nanoparticles could enable the gatherings to be coordinated to a tumor site by an outer magnet and could likewise bolster symptomatic imaging.
Past the movement of the medications, the plasmonic impacts of the gold nanoparticles could warm the nanoparticles when they are subjected to light, assaulting the growth cells during a time course.
Notwithstanding the potential therapeutic uses, the self-gathering method could have applications in optics, optoelectronics, attractive advancements, detecting materials and gadgets, catalysis and nanotechnology. The strategy could likewise prompt new essential research in crystallization energy, utilizing the self-get-together procedure to make “fake precious stones” held together by polymer chains.
Lin’s lab has dealt with amphiphilic star-formed piece polymers for quite a long while, including new highlights and investigating new abilities for nanoparticle frameworks.
He stated, “Our work gives a planned procedure that permits the control of both the external square and the inward piece of a star-formed square co-polymer.”
“Our key commitment in this work is to wisely set up a star-molded piece co-polymer in which the inward square has the capacity to facilitate with metal antecedents while the external piece permits photograph responsive materials to collaborate, which thus renders the creating of photograph responsive gold nanoparticles for light-empowered reversible and dependable self-get together.”
Journal Reference
- Chen, Y., Wang, Z., He, Y., Yoon, Y. J., Jung, J., Zhang, G., & Lin, Z. (2018). Light-enabled reversible self-assembly and tunable optical properties of stable hairy nanoparticles. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 115(7), E1391-E1400. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1714748115
