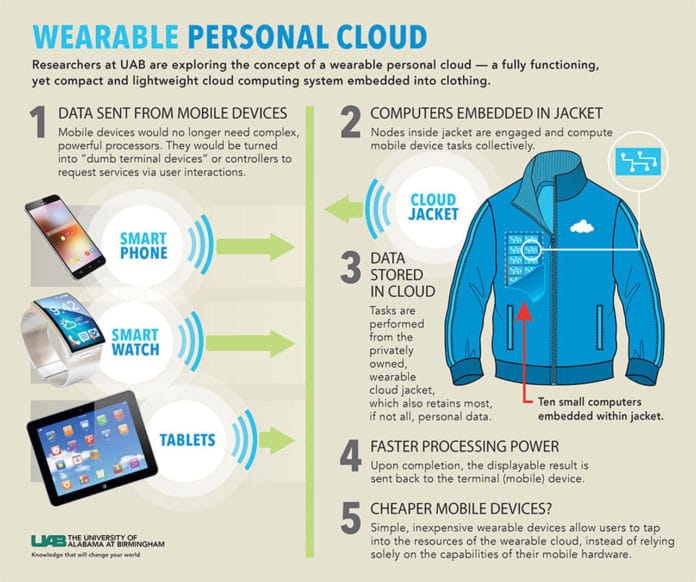
Scientists from the University of Alabama at Birmingham are exploring a new form of a cloud computing system. It is the concept of a wearable personal cloud that is fully functional, compact, and lightweight. It will come in the form of a wearable cloud jacket.
Scientists first collect Raspberry Pi’s computer, a winter jacket, three power banks, and a small remote touch screen display. Scientists developed a wearable system that combines all mobile computing solutions by using all these components. Hence, it creates a smart device with a novel cloud computing system. The cloud jacket enables users to tap into the resources of the wearable cloud rather than depending on the capabilities of their mobile hardware.
Ragib Hasan said, “If you want to have a smartwatch, smartphone, an exercise tracker and smart glasses, you need individual expensive devices that aren’t working together. So, why not have a computational platform with you that supports many forms of mobile and wearable devices? Then all of these capabilities can become really inexpensive.” (Ragib Hasan is a Ph.D. assistant professor of computer and information sciences at the UAB College of Arts and Sciences.)
Most mobile and wearable devices are made with nearly 10 times slower processors than desktop or laptop processors. Thus, they limit applications that run on them. Hence, newer versions of mobile and wearable devices are continuously released to keep up with changes in technology. But they are expensive.
To complete resource limitations, many mobile applications are powered by cloud servers. But, they require constant communication over the internet. Mobile and wearable device users need to upload all personal data to remote public clouds or local cloud data centers without the knowledge of where their personal data is actually being stored.
Rasib Khan, Ph.D., a recent postdoctoral graduate student, said, “Our overall approach is to create a generic atmosphere or platform that users can customize to fit their needs. The wearable cloud can act as an application platform. So instead of modifying or having to upgrade hardware, this wearable model provides a platform, and developers can build anything on top of it.”
Because of this wearable cloud, mobile and wearable devices will no longer need complex, powerful processors. Thus, this wearable cloud could provide the experience of a smart device by turning into dumb terminal devices or controllers. If a user connects the terminal device via Bluetooth or WiFi, he utilizes the devices to request services via a user-intuitive display and interactions. The computational task is then sent to the wearable private cloud.
This new cloud computing concept is not limited to clothing. The system model enables the personal cloud to boost any item carried on a daily basis, from a jacket to a briefcase, purse, or backpack.
The Nodes inside the jacket are engaged and compute the task collectively. Upon completion, the displayable result is sent back to the terminal device. The tasks are performed from the privately owned wearable cloud jacket, which also retains most if not all, personal data.
Hasan claimed, “Once you have turned everything else into a ‘dumb device, the wearable cloud becomes the smart one. The application paradigm becomes much more simple and brings everything together. Instead of individual solutions, now you have everything as a composite solution.”
Also Read: Olli, a 3D Printed, Self-driving Minibus
“With seven to 10 people wearing such a cloud together, they create what we call a hyper-cloud, a much more powerful engine. The jacket can also act as a micro or pico cell tower. All of its capabilities can be shared on a private network with other devices via WiFi or Bluetooth. If a first responder is out on the field and doesn’t have complete information to act on a mission, but someone else does, it can be share and update through the cloud in real-time.”
If any disaster occurs and first responders enter a damaged building. They may have blueprints of what the building looked like prior to the incident. But only those inside know what areas are now damaged or where an injured person does locate. Anyone can access the cloud by pairing the wearable cloud with a device like Google Glass or night vision goggles. They can also see whatever the person wearing the cloud sees in real-time. They will not need any platform or device-specific hardware and software at that time.
“Another potential application area that we are looking into is hospital gowns. When a patient comes in, they connect to monitors to obtain heart rate, blood pressure, and other vitals. Whenever a patient goes to the restroom or needs to be move around, they have to take everything off or maneuver around with a large pole carrying all of the connected devices. Instead, we are putting sensors inside a vest that can be placed over the hospital gown itself. There will be a small version of the wearable cloud within the vest. Thus the vest itself can collect information, like a patient’s temperature,” said Hasan.
According to scientists, this new cloud computing system technology solution could aid in various ways. It may be useful for first responders to communicate and share information during disasters to how soldiers communicate on the battlefield.