Different nanocarbons are being studied and utilized for purifying water and wastewater by adsorbing dyes, gases, organic compounds, and toxic metal ions. These nanocarbons can adsorb massive metal particles, similar to lead and mercury, onto their surfaces through molecular attraction forces. In any case, this attraction is weak. Thus they aren’t productive adsorbents.
To improve adsorption, scientists are considering adding molecules to the nanocarbons, like amino groups, that form stronger chemical bonds with heavy metals.
Scientists from Nagoya University, recently have come up with a one-step fabrication process to improve the ability of nanocarbons to remove toxic heavy metal ions from water. It also helps efforts to promote universal access to clean water.
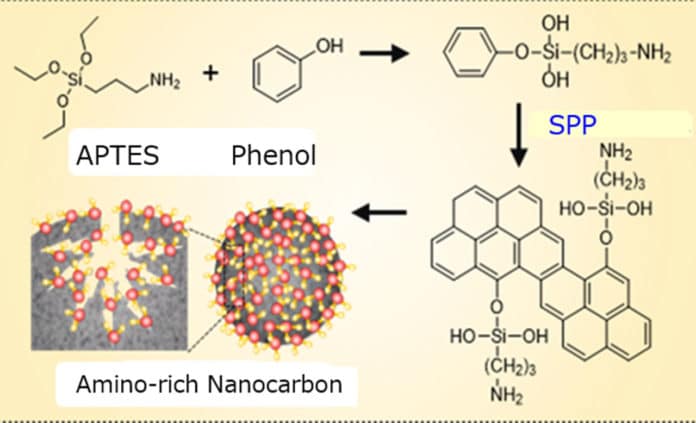
To develop this new method, scientists mixed phenol with a compound called APTES, as a source of amino groups. They then placed this mixture in a glass chamber and exposed to a high voltage, creating a plasma in liquid. For this purpose, they used the solution plasma process. Black precipitates of amino-modified carbons formed and were collected, washed, and dried.
Multiple tests have shown that amino groups had evenly distributed over the nanocarbon surface, including into its slit-like pores.
Saito said, “Our single-step process facilitates the bonding of amino groups on both outer and inner surfaces of the porous nanocarbon. This drastically increased their adsorption capacity compared to a nanocarbon on its own.”
Scientists put amino-modified nanocarbons through ten cycles of adsorbing copper, zinc, and cadmium metal ions, washing them between each cycle. Although the capacity to adsorb metal ions decreased with repetitive sequences, the reduction was small, making them relatively stable for repeated use.
Finally, the team compared their amino-modified nanocarbons with five other synthesized by conventional methods. Their nanocarbon had the highest adsorption capacity for the metal ions tested, indicating there are more amino groups on their nanocarbon than the others.
Saito said, “Our process could help reduce the costs of water purification and bring us closer to achieving universal and equitable access to safe and affordable drinking water for all by 2030.”
Reference:
- Liquid-Phase Plasma-Assisted in Situ Synthesis of Amino-Rich Nanocarbon for Transition Metal Ion Adsorption. DOI:10.1021/acsanm.9b01915