Scientists are working on a new way to detect blood clots and assess anti-blood-clotting drug effects.
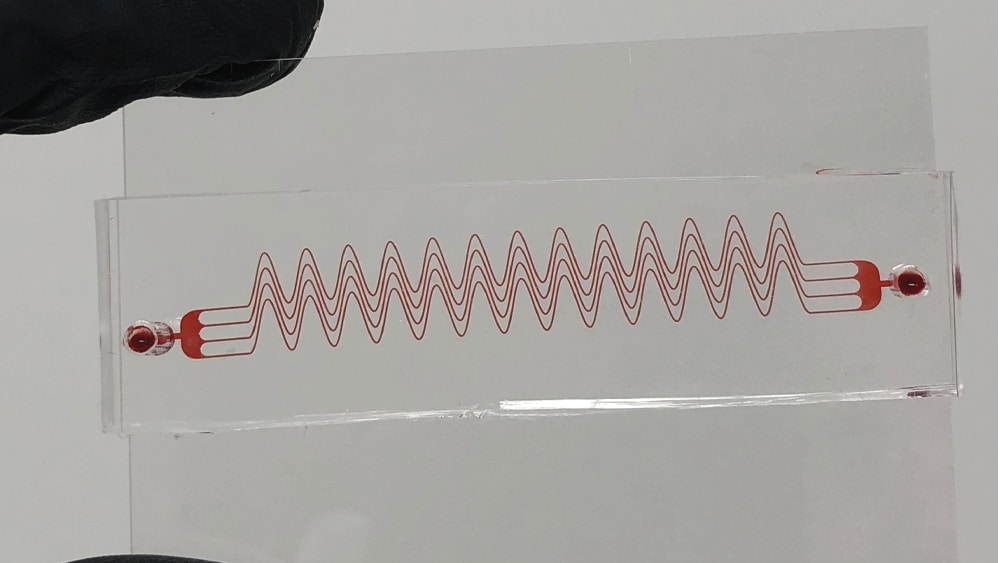
To address this problem in a new angle, scientists in Jain’s lab at Texas A&M have developed a microdevice that acts as a tortuous blood vessel.
For testing, scientists created a diseased microenvironment in which blood may rapidly clot during flow—the microdevice as able to detect clotting disorders.
Scientists noted, “We can see several applications for the device, including critical care units and military trauma care units.”
“It can be used in the detection of clotting disorders and used in precision medicine where you would want to monitor pro-thrombotic or anti-thrombotic therapies and optimize the therapeutic approach.”
Currently used blood clotting devices are expensive, time-consuming, and unreliable. They also need a skilled technician. In contrast, this newly developed tortuosity based microfluidic system doesn’t require costly chemicals. Plus, it is quick and gives results in 10-15 minutes, uses low blood sample volume, and is easy to operate.
Journal Reference:
- Luna, Tortuosity-powered microfluidic device for assessment of thrombosis and antithrombotic therapy in whole blood. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-62768-4