Using Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) and extreme adaptive-optics systems, Monash astrophysicists reported the world’s first discovery on the sighting of a second new ‘baby’ planet inside a gas and dust gap.
This is for the first time, scientists have reported about the discovery of a new planet inside a protoplanetary disc.
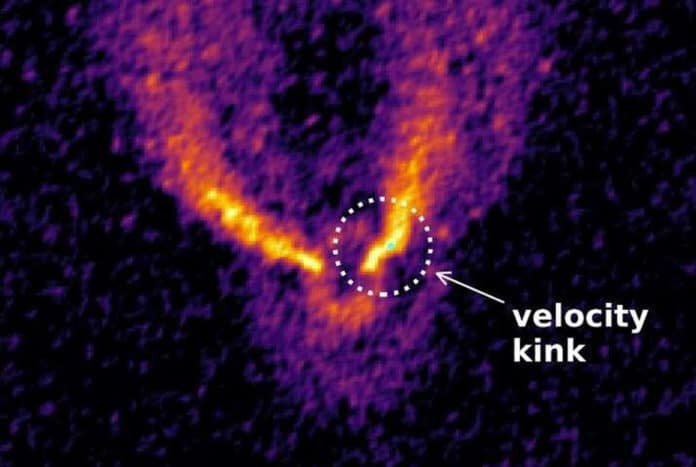
The new baby planet was found by mapping the flow of gas around the star, and looking for where the flow is disturbed by the presence of a planet—much like finding a submerged rock in a river from the disturbance to the water around it.
Lead study author Dr. Christophe Pinte, an ARC Future Fellow at the Monash School of Physics and Astronomy said in 2015, the ALMA telescope first observed the insides of a `protoplanetary disc’—the birthplace of planets—around a nearby young star.
“What it saw was a stunning series of mysterious rings and gaps,” Dr. Pinte said.
“The origin of these gaps has been the subject of much debate,” he said.
“Now we have the first direct evidence that a baby planet is responsible for carving one of these gaps in the disc of dust and gas swirling around the young star HD97048.”
Study co-author Associate Professor Daniel Price, also an ARC Future Fellow at the School said the latest discovery adds to only a handful of known baby planets.
“Our study establishes for the first time a firm link between baby planets and the gaps seen in discs around young stars,” Associate Professor Price said.
“There is a lot of debate about whether baby planets are really responsible for causing these gaps.”
Details about the new observation are published today in the prestigious journal Nature Astronomy.
References:
- Kinematic detection of a planet carving a gap in a protoplanetary disk.
- Kinematic Evidence for an Embedded Protoplanet in a Circumstellar Disk.