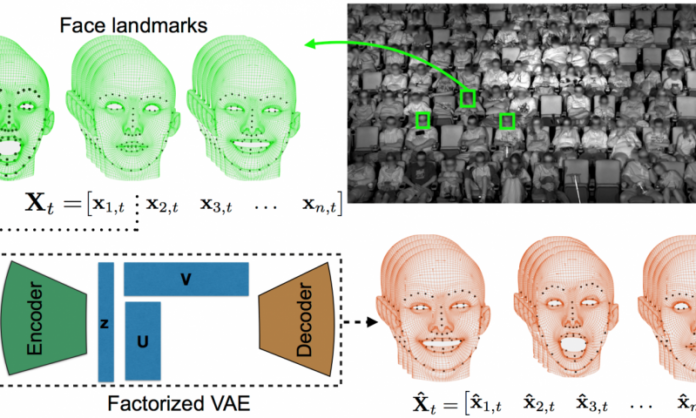
The scientist of Disney research center developed a new method, that access composite audience reactions to movies via facial expression. Named as Factorized Variational Autoencoder or FVAEs, the method has the potential to reliably predict a viewer’s facial expressions for the rest of the movie after observing an audience within few minutes.
Zhiwei Deng a Ph.D. student from Simon Fraser University said, “The FVAEs were able to learn concepts such as smiling and laughing on their own. What’s more, they were able to show how these facial expressions correlated with humorous scenes.”
FVAEs intimate an explicit ability to certain predict a viewer’s facial expression for the oddest of the movie after observing an audience member for only a few minutes. Still, results are exploratory.
Voice Precedent of Disney Research Markus Gross said, “We are all awash in data, so it is critical to find techniques that discover patterns automatically, our research shows that deep learning techniques, which use neural networks and have revolutionized the field of artificial intelligence, are effective at reducing data while capturing its hidden patterns.”
For testing, researchers implement this method to 150 showing of 9 mainstream movies. They choose 400-seat theater that was embedded with four infrared cameras to overseas faces of assemblage. Almost 3,179 audience members and 16 million facial landmarks were detected.
Scientist Peter Carr said, “It’s more data than a human is going to look through, that’s where computers come in- to summarize the data without losing important details.”
FVAEs look for audience members who exhibit similar facial expressions throughout the entire movie. It then learns set of hackneyed reaction from the entire audience. In actual, it looks for audience members who display similar facial expressions throughout the entire movie. After that, it learns for a set of hackneyed reaction from the entire audience.
It also induces how audience member should be reacting to given movie based on strong inter-dependency in revulsion between audience members.
Scientist Stephan Mandt said, “FVAEs to predict a viewer’s facial expression for an entire movie based on only a few minutes of observations”
The pattern recognition technique inside it does not only limited to faces but also used on any time series data collected from a group of objects.
Yisong Yue, an assistant professor of computing and mathematical sciences from the California Institute of Technology said, “Once a model is learned, we can generate artificial data that looks realistic. For instance, if FVAEs were used to analyze a forest- noting differences in how trees respond to wind based on their type and size as well as wind speed -those models could be used to simulate a forest in animation.”