A youthful tyke goes through weekdays with her grandma down the road while her folks work. Another goes to an unlicensed day mind focus keep running by a neighbor. A third is with his stay-at-home father. A fourth is looked after by a private babysitter in the solace of her own home.
Specialists have since quite a while ago concentrated how little kids develop and learn in formal, top-notch preschool programs, and have discovered that they grow better dialect, math, and education aptitudes and additionally more grounded social and passionate associations than the individuals who don’t go to.
However little is thought about the youngsters who are taken care of under casual courses of action including neighbors, relatives, companions, or babysitters, despite the fact that these cover 40 percent of kids in Massachusetts.
Two Harvard scientists are attempting to make sense of that.
Harvard Graduate School of Education (HGSE) teachers Nonie Lesaux and Stephanie Jones, both formative therapists, are propelling a driven investigation to take after 5,000 kids, ages 3 and 4, for a long time. The examination will track a few understudies when their grade school years, and maybe into adulthood. The associate, enlisted from 168 groups, is intended to mirror the changing socioeconomics of youngsters over the state.
Through the Early Learning Study at Harvard, Lesaux and Jones plan to refresh the science around tyke mind by inspecting the connections between kids’ advancement and the attributes of the instructive and care settings where they spend their developmental years, be those relatives’ homes or unlicensed childcare focuses or, for examination, neighborhood Head Starts and Montessori preschools.
Lesaux, the Juliana W. and William Foss Thompson Professor of Education said, “There are a lot of unanswered questions that parents, communities, policymakers, and school districts are grappling with. And we don’t have enough specific information to drive 21st-century policy in early education.”
Jones, a professor of education said, “Our body of evidence is outdated. It’s based on studies from the 1960s, primarily. It also focuses primarily on the center-based, licensed, formal early education offerings. And what’s missing is the settings described as informal or non-licensed that are offered outside the formal centers. We just don’t know very much about them.”
In early youth training, the most compelling examination incorporates the Perry Preschool Study, led by the mid-1960s at a Michigan preschool, and the Abecedarian Project led by the 1970s in North Carolina. The two examinations, which took after kids into their grown-up years, found that the youngsters who got preschool training flourished more than the individuals who did not. The preschool youngsters earned more cash, were more well behaved, will probably move on from secondary school, and even were more beneficial.

Led by the Saul Zaentz Early Education Initiative at the Ed School, the new Harvard consider is intended to be notable in scope and phenomenal in reach, said Lesaux.
Out of the blue, analysts will think about casual care settings and connection their highlights to youngsters’ social and enthusiastic advancement. The scientists intend to associate what they find out about early math, education, and dialect abilities with information that mirrors the present populaces and current settings. A recent report, bolstered by the U.S. Bureau of Education, inspected the nature of casual preschool settings versus formal settings, however, utilized decade-old information.
Prior investigations demonstrated that youngsters who invest more energy in childcare focuses make progress in dialect and psychological aptitudes, in any case, contingent upon the quantity of hours and the qualities of the settings, may likewise grow more behavioral issues than kids who spend fewer hours there.
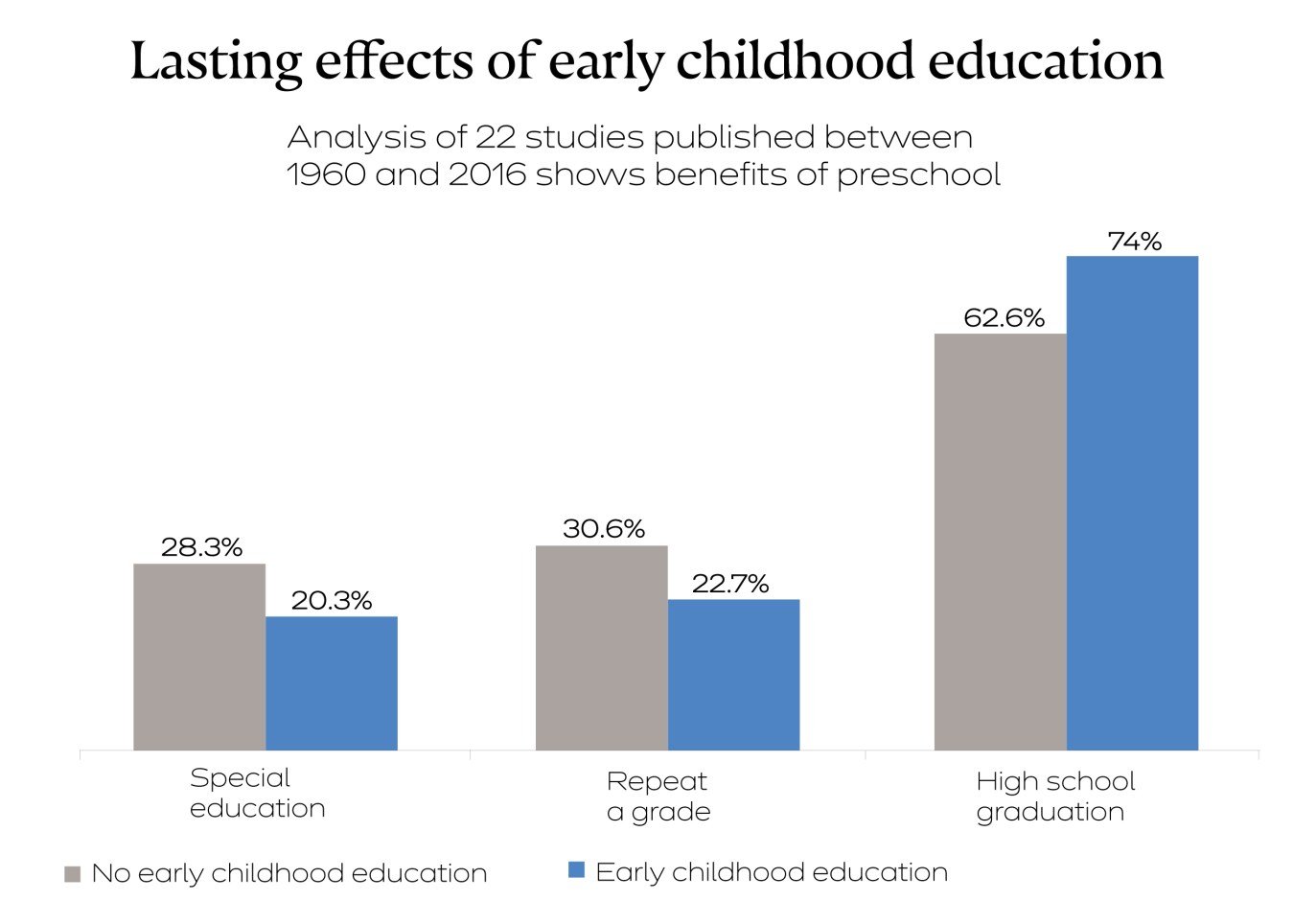
A current report drove by Dana Charles McCoy at HGSE broke down 22 contemplates on early youth instruction distributed in the vicinity of 1960 and 2016 and found that the advantages of early youth training have enduring impacts. The examination presumed that the individuals who went to preschool were less inclined to be set in specialized curriculum classes and be required to rehash a review, and more prone to move on from secondary school.
In the new investigation, scientists will survey youngsters’ advance in dialect, early math, and proficiency aptitudes, yet in addition their social, enthusiastic, neurophysiological, and psychological improvement by looking at their cooperations with other kids and their associations with grown-ups in their lives. Lesaux and Jones trust the Early Learning Study inevitably will affect national instructive approach.
“It absolutely can possibly change the national discussion about early instruction,” said Lesaux. “It will be the primary look, statewide, at the two youngsters and the assortment of early instruction settings.”
The scientists additionally would like to take in why a few advances from early instruction persevere for youngsters while others blur in the main years of primary school.
“A great deal of the focal point of different investigations is the fadeout of scholastic aptitudes,” said Tara Chiatovich, the Zaentz Initiative’s exploration researcher, and the examination’s director. “We need to perceive what occurs with picks up in social and enthusiastic improvement, which may tend to hold on for some time more than scholastic aptitudes. We additionally need to see where those increases are kept up or undermined in the early years of grade school.”
Research recommends that superb early instruction has an essential effect on youngsters’ lives, yet just a minority of the advantage from it. Of the 60 percent selected in some type of preschool across the country, just 20 percent go to what might be viewed as an excellent program. The highlights of astounding early tutoring incorporate little gathering sizes, low grown-up to-tyke proportions, and parental figure abilities.
“Numerous families don’t approach a brilliant early instruction encounter for their kid,” said Jones. “Furthermore, we know from many years of research that what truly impacts results for youngsters is an introduction to a high caliber. It’s intended to make everything fair, and we’re not there yet.”
The 2006 Study of Early Child Care and Youth Development by the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development found a solid connection between’s higher-quality youngster care and school availability. Youngsters in excellent settings were found to have more extensive vocabularies, combined with more grounded dialect and early math aptitudes. They likewise, by and large, were more agreeable than peers in low-quality preschool programs.
Fantastic early instruction is particularly critical for kids from helpless populaces, said Lesaux and Jones. Stress and difficulty influence kids’ learning. Research has demonstrated that youngsters from low-pay families advantage the most from top-notch early instruction, but the development toward all-inclusive amazing preschool has been a difficult task broadly.
“It has been difficult to fabricate the political will to finance top-notch preschool encounters,” said Lesaux. “As a nation, we’re not in understanding that it’s justified regardless of the venture.”
The new examination has started a family unit overview of guardians crosswise over Massachusetts to enroll kids and families. On a current evening, Yvonne Illich, a field laborer with Abt Associates, an exploration firm cooperating with Harvard to direct the examination, enjoyed a reprieve from thumping on entryways in Lexington, one of her assigned work zones.
“Guardians ask me, ‘How might this benefit my youngster?,’ ‘How might this benefit my family?‘ ” said Illich. “I disclose to them they can perceive how their youngster is developing and creating. Guardians need to ensure their youngsters are having the best kick off throughout everyday life.”
Notwithstanding propelling an institute for proficient learning in early youth instruction to sharpen policymakers and professionals’ mastery, the Zaentz activity has started an association program to construct another pipeline of pioneers in the field.
Lesaux and Jones trust that the investigation’s possible discoveries will move the needle in the level-headed discussion on all inclusive superb preschool. With the quantity of working families developing broadly, tyke mind is a need, said Jones, and having progressively and better alternatives is vital.
“We can disregard these open doors, or we can contribute and make a move by taking a shot at quality,” Jones said. “Regardless of whether it’s justified, despite all the trouble isn’t the inquiry; it’s the means by which to amplify it.”
By reinforcing early instruction broadly, the examination additionally could fortify families and society, as a rule, said Lesaux.
“In a top-notch preschool, kids are candidly more managed, they improve the situation by their conduct, they convey more to connections with grown-ups, and grown-ups like both working and realizing that their youngster is sheltered and solid,” said Lesaux.
“Kids just get one begin,” she included. “Pay now or pay later. We needn’t bother with any more information in this nation about the impacts of a lousy instruction on the life of an individual and the life of a group and the quality of the general public.”
