Scientists at Mohali based research institute, the Center of Innovative and Applied Bioprocessing (CIAB), have made a breakthrough by developing an antimicrobial sunscreen from metal oxide nano-composites developed from agricultural waste-based lignin. In this study, the lignin, which is otherwise considered as a waste, has been converted into a value added product.
Lignin is a natural organic biopolymer rich in polyphenolic groups which make it an ideal candidate for various industrial applications. Lignin is a byproduct of paper and pulp industry and is extracted from wheat and rice husk. It is often thrown into water bodies or openly burnt in the field at the end of crop harvest.
Scientists discovered that lignin offered an easy and sustainable synthesis of zinc oxide nano-composites in the water-ethanol composition. The synthesis did not involve any toxic solvent or catalyst, thus, making the process environment-friendly.
Lignin-based nano-composites have commercial value because of its UV protective, antioxidant, and antimicrobial properties. The ZnO nanoparticles were synthesized using Kraft and alkali lignin as a sole capping and reducing agent. Only the zinc oxide precursor salt and the lignin were used for nano-composite synthesis.
Usually, the synthesis of metal oxide nanoparticles requires harsh techniques, including toxic chemicals, as well as heating at very high temperatures (300-400°C). However, scientists at CIAB used a simple, green, and industrially feasible method to design lignin-based ZnO nanoparticles.
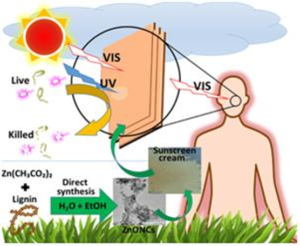
Scientists used agro-waste based lignin to convert ZnO in a single step into nano-composites with promising UV protective and antimicrobial potential. Such nano-composites showed a broad range of antimicrobial activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
The lignin-derived nano-formulations showed excellent UV- protective efficiency when used as an additive in commonly used body creams. They are expected to find potential applications as UV-blocking and antimicrobial ingredients for use in versatile industrial products.
The research work has been published in the Journal of Materials Chemistry B.
