Stroke, known as a leading cause of long-term disability, is a sudden loss of brain function. It occurs when blood flow to an area of the brain is cut off. In this situation, brain cells are deprived of oxygen and begin to die. And thus, abilities controlled by that area of the brain such as memory and muscle control are lost.
Especially for the patients who have a stroke, researchers at the UNIST have developed a new robotic tool to improve the mobility of patients surviving a stroke. As the stroke consequences, the survivors are often left with muscle over-activity, including spasticity, characterized by tight or stiff muscles and an inability to control those muscles.
According to scientists, this newly developed robotic tool may help in assessing muscle overactivity and movement dysfunction in survivors of stroke. In real, it is the rehabilitation robotic system that quantitatively measures the three degree-of-freedom (DOF) impedance of human forearm and wrist in minutes.
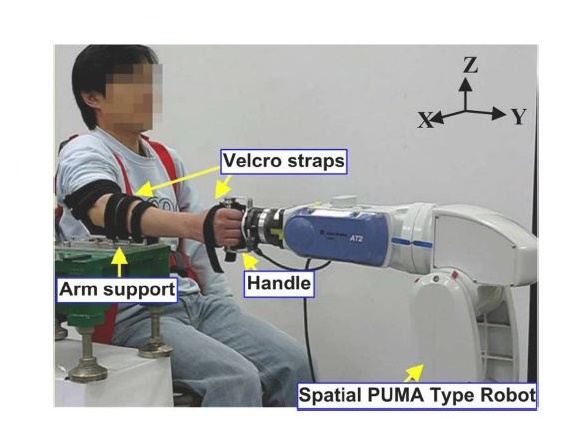
forearm and wrist impedance.
Using their impedance estimation device, entitled the distal internal model based impedance control (dIMBIC) based method, the team was able to accurately characterize the 3 DOF forearm and wrist impedance, including inertia, damping, and stiffness, for the first time.
Professor Sang Hoon Kang of Mechanical, Aerospace and Nuclear Engineering at UNIST said, “The dIMBIC-based method can be used to assist in the quantitative and objective evaluation of neurological disorders, like a stroke. Findings from this study will open a new chapter in robot-assisted rehabilitation in the workplace accident rehabilitation hospitals, as well as in nursing homes and assisted living facilities.”
According to the researchers, the proposed 3 DOF impedance estimation may promote wrist and forearm motor control studies and complement the diagnosis of the alteration in wrist and forearm resistance post-stroke by providing objective impedance values including cross-coupled terms.
