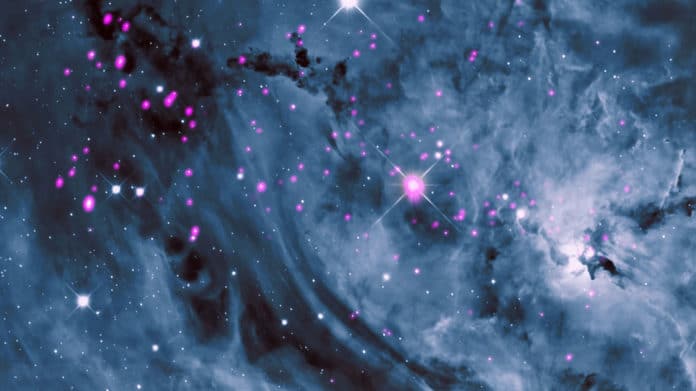
Also known as Messier 8, the Lagoon nebula is the prominent region of star formation. Located about 4,000 light-years away, the Lagoon Nebula, aka NGC 6523, is a giant gas cloud. In this gas cloud, a cluster of young, hot stars ionizes the nearby gas.
The atoms in the gas recombine to create the light emitted by the nebula. Interstellar dust within the nebula absorbs some light and appears almost to divide the nebula, thus producing a lagoon-like shape.
Many infant stars give off copious amounts of high-energy light, including X-rays, seen in the Chandra data (pink). The X-ray data have been combined with an optical image of Messier 8 from the Mt. Lemmon Sky Center in Arizona (blue and white).
The nebula contains several Bok globules. In addition, it includes a funnel-like or tornado-like structure caused by hot stars that emanates ultraviolet light, heating and ionizing gases on the surface of the nebula.