Internal Combustion Engines are widely used in vehicles. It uses fuel in confined spaces. The engine has portability and is more convenient than electricity, hybrid vehicles, etc. But the major drawback of these engines is the pollution that they put out. Internal Combustion Engines creates air pollution in large amount.
To replace this engine, many engineers are working on new technologies like electric motors, hybrid power trains, hydrogen fuel cells, and even cars that run on compressed air. But none of these technologies are efficient. So, we need a better internal combustion engine.
Here is the good news: Better internal combustion engines are on the way.
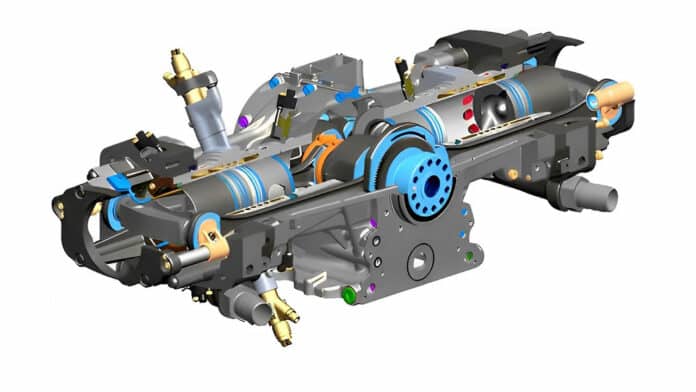
A company called Ecomotor is developing a new Engine named as Opposed-Piston-Opposed-Cylinder Engine. Opposed- Piston-Opposed-Cylinder (OPOC) Engine is the most exciting new type of internal combustion engine.
The architecture of the OPOC Engine:
The OPOC engine is an opposed-piston, opposed-cylinder, 2-stroke engine. It consists of two cylinders with a piston at both ends. It has no cylinder head, so there are no valves.
Each piston travels about half the distance of a cylinder in a conventional engine. As compared to other conventional engines, the OPOC has a drastically small size.
The opposed cylinder with the piston has very low bearing loads. It means there will be less friction as compared to the conventional engine.
Each piston in the engine has a single crankshaft with connecting rods (inner pistons have short connecting rods, and the opposing outer pistons have long connecting rods).
When the pistons move together, it compresses the intake charge for ignition. It simply means the engine has a high power density.
Specifications of OPOC:
- Dry weight: 296 pounds
- Dimensions: 22.8 x 41.3 x 18.5 (inches), Length x Width x Height
- Cylinder bore: 100 millimeters
- 325 horsepower at 3500 rpm.
- Torque: 664-pound-feet at 2100 rpm
- Power density: 1.1 horsepower/pound
Features of OPOC:
- Smaller size
- Lighter weight
- Fewer parts
- Higher efficiency
- Unmatched power density
- A truly modular design
Working of OPOC Engine:
The engine makes a complete cycle with two-piston movements. It intakes and exhausts simultaneously during the initiation of the compression stroke and after the combustion stroke. This process allows the engines to give very high power for their weight.