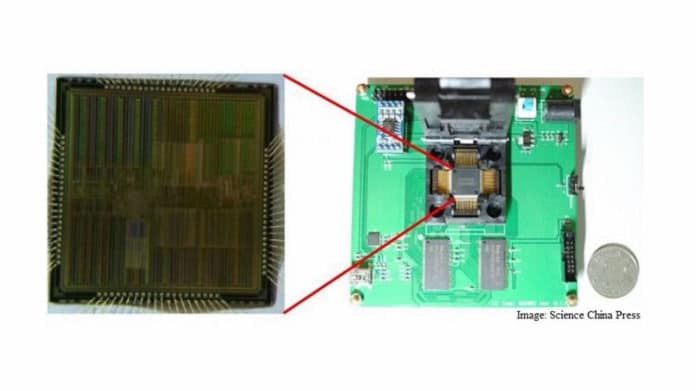
Researchers from the University of Zhejiang and the University of Hangzhou Dianzi in China have created a revolutionary information chip, which will enable the operation of harmoniously connected intelligent algorithms on a small device called ‘Darwin NPU (Neural Processing Unit)’. ‘Darwin NPU’ is a hardware co-processor which is neuromorphic got from Spiking Neural Networks (SNN), made by Standard CMOS (Complimentary metal oxide Semiconductor).
Artificial Neuron Network (ANN) is a kind of data processor, works on principles of biological brains and mainly used in fields of pattern recognition, automatic control decision support system, signal processing, and artificial intelligence. SNN (Simulated Neural Network) is a kind of biologically inspired ANN, which processes data based on discrete-time spikes. SNN’s have that kind of ability to have a more high-performance-power ratio than the classic ANN’s.
The development of several intelligent devices that offer services and allow users to access easily have increased challenges of making it possible to operate harmoniously connected intelligent algorithms on small devices. The ‘Darwin NPU’ now answers for all of these challenges and allows intelligent algorithms to run on constrained low-power, small embedded device resources.
The NPU also proves that the possibility of developing spiking Neural Networks in resources starved the embedded systems. It can be customized for different functionalities as configured by the user.
“Since it uses spikes for information processing and transmission, similar to biological neural networks, it may be suitable for analysis and processing of biological spiking neural signals, and building brain-computer interface systems by interfacing with animal and human brains“, said author.
- It is made from 180 nm standard CMOS process, supporting a maximum of 2048 neurons, more than 4 million synapses, and different possible synaptic delays.
- It consumes 0.84 W/MHz with 1.8v power supply for typical applications.
- Based on open-source, Open Core minsoc project, it is integrated with RISC CPU to form a complete System-on-chip (SOC). SOC consists of a local bus, 64 kb SRAM, SPI flash, UART controller and SDRAM controller.
- ‘Darwin NPU’ can achieve similar average latency at a lower clock speed and moderately better classification accuracy in terms of handwritten digit recognition.
- It supports the flexible configuration of a multitude of parameters of the neural network. Therefore, it can be used for implementing different functionalities configured by the user.
- It has potential applications that include intelligent hardware systems, robotics, brain-computer interfaces, and others.
- It uses spikes for processing of information and transmission, which is just similar to biological neural networks.
- Shows higher accuracy, when it comes to the decoding of Electroencephalogram (EEG) signals.
Ma De, a doctoral student from Hangzhou Dianzi University said,” one of the challenges in making the ‘Darwin NPU’ is to achieve large-scale neurons and synapses on a very tiny chip. With specialized training, the ‘Darwin NPU’ can familiarize itself with the EGG of the operator. It will make a response by activating corresponding neurons exposed to familiar external stimuli.”